Raw Material Handling
Ensure a seamless raw material handling process with our efficient…
Ensure a seamless raw material handling process with our efficient…
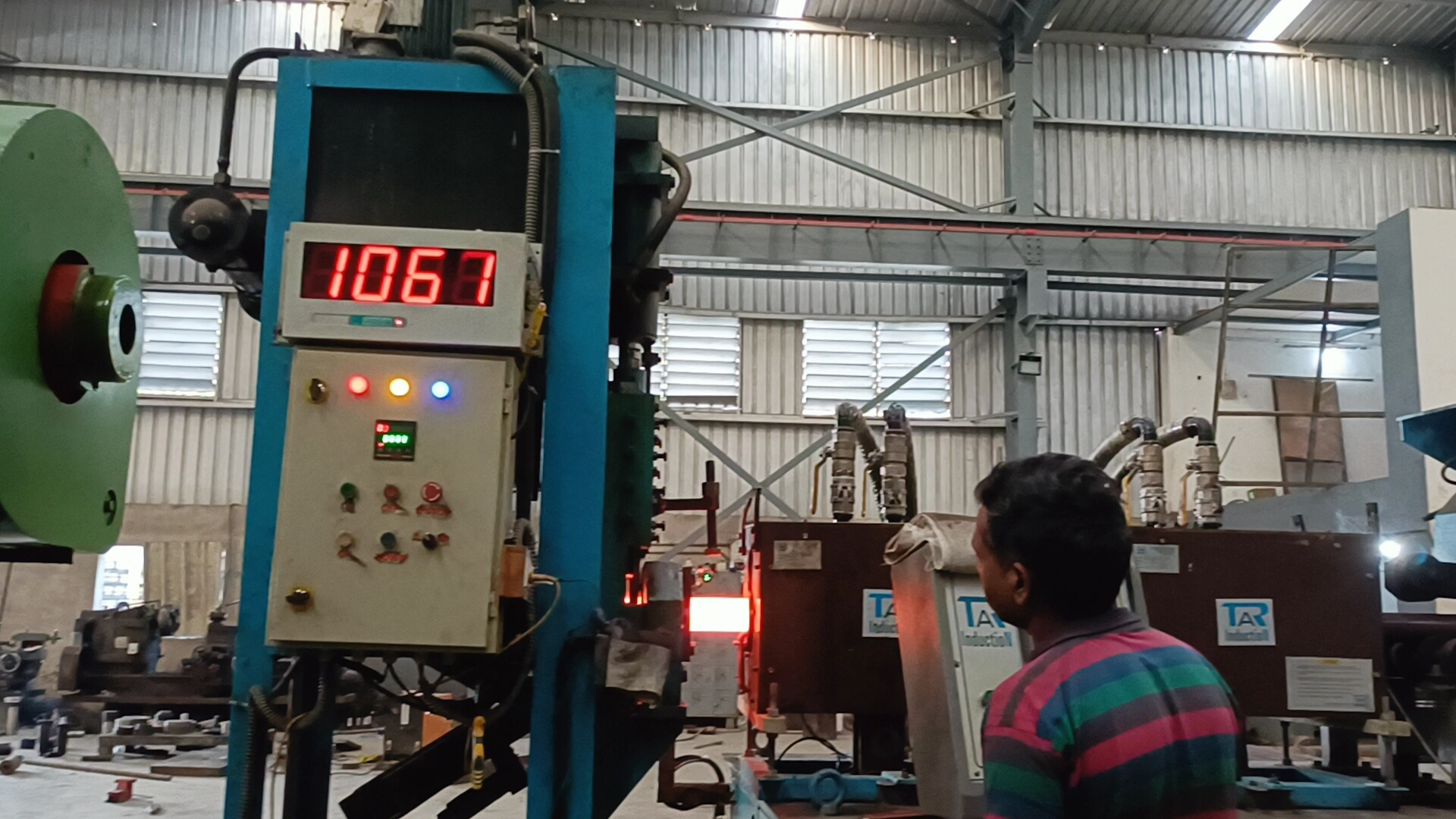
Optimize steel heating processes with our advanced induction heating facilities…

Our cutting facilities offer precision hot shearing and bar cutting…
We provide state-of-the-art forging facilities with advanced presses and ring…

Enhance steel durability with our heat treatment solutions, including annealing,…
Achieve high precision with our CNC finishing services, delivering expertly…

7 min Read
When it comes to manufacturing metal components, two primary methods dominate the industry: forging and casting. Both processes offer unique advantages and are suitable for different applications. However, the choice between forging and casting can significantly impact the final product’s strength, durability, cost, and overall performance. In this article, we will compare forging and casting, exploring their key differences, advantages, and best use cases for industrial applications.
Forging is a manufacturing process that involves shaping metal using compressive forces, typically applied through hammers, presses, or dies. The process can be performed at different temperatures:
Casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold, allowing it to solidify into the desired shape. The casting process can be categorized into various types:
| Feature | Forging | Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Strength & Durability | High | Moderate |
| Design Complexity | Limited | High |
| Material Waste | Higher | Lower |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Production Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Defect Rate | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal for High-Stress Applications | Yes | No |
Forging is the best choice when strength, reliability, and resistance to wear and fatigue are top priorities. Common applications include:
Casting is preferred when intricate designs, cost-effectiveness in mass production, and material versatility are essential. Typical applications include:
In some cases, manufacturers use both forging and casting to maximize benefits. For example:
Both forging and casting offer valuable benefits in industrial applications. Forging is the superior choice for high-strength, high-reliability components, whereas casting is ideal for complex shapes and mass production. Selecting the right process depends on your industry’s specific needs, budget, and performance requirements. Understanding these differences ensures better decision-making for optimizing production and product quality.
For businesses seeking precision manufacturing solutions, partnering with an experienced forging or casting provider ensures superior component quality, cost efficiency, and long-term reliability.
Get in touch with our experts today
