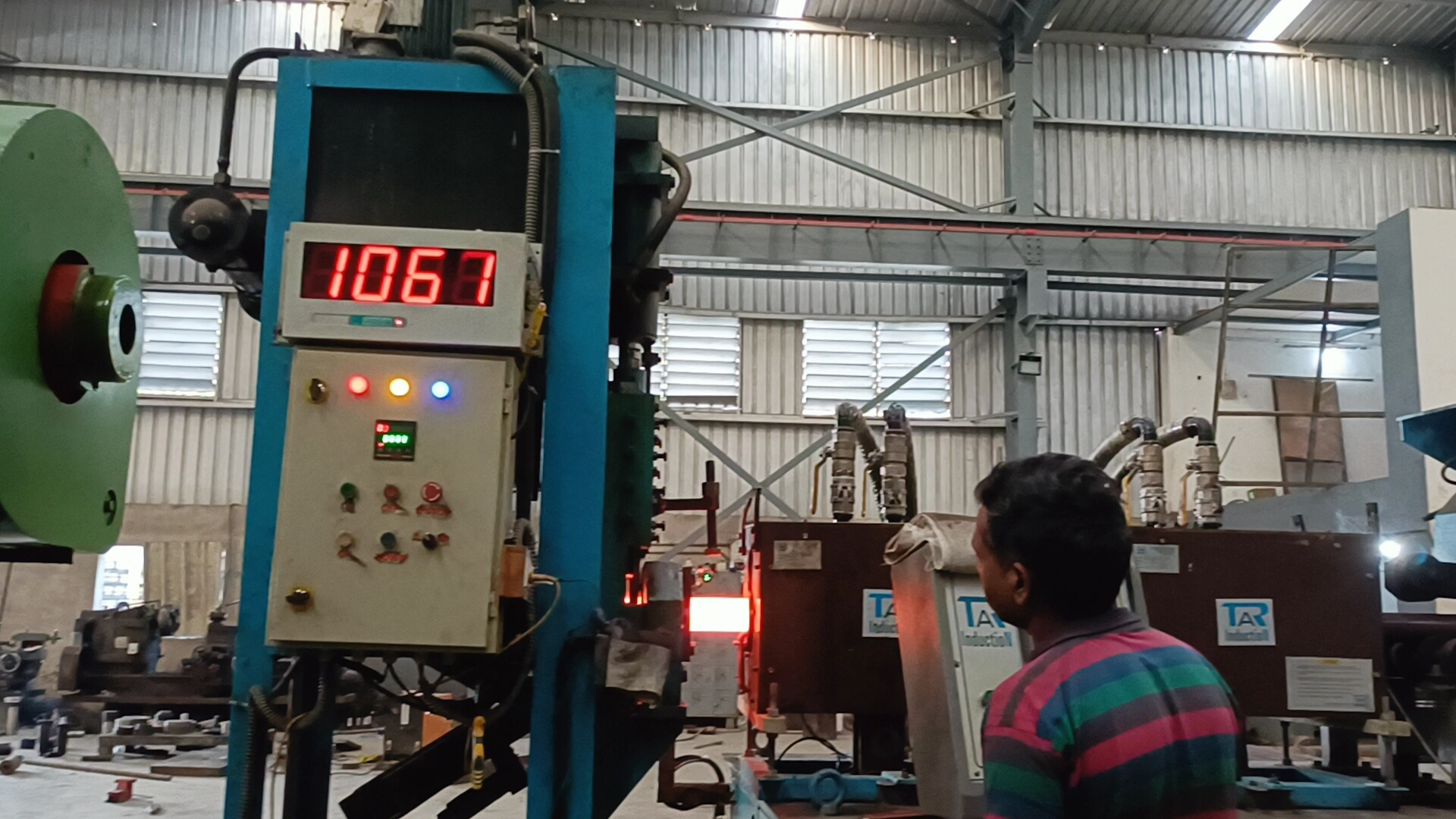
The automotive industry relies heavily on forged components due to their superior strength, durability, and reliability. Forging, a manufacturing process that shapes metal through compressive forces, produces parts capable of withstanding the extreme stresses and demanding conditions within vehicles. This article explores the top applications of forged auto components, highlighting their critical roles in ensuring vehicle performance, safety, and longevity.
Engine Components:
Forged components play a vital role in the heart of any vehicle – the engine. The high stresses and temperatures within the engine demand parts that can withstand these harsh conditions, making forging the ideal manufacturing process. Key forged engine components include:
- Connecting Rods: These crucial links between the pistons and crankshaft experience immense forces. Forged connecting rods offer superior strength and fatigue resistance compared to cast or powdered metal alternatives, preventing engine failure under stress.
- Crankshafts: Converting the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion, crankshafts endure significant torsional and bending stresses. Forged crankshafts provide the necessary strength and durability for reliable engine operation.
- Pistons: While some pistons are cast, forged pistons are often used in high-performance engines due to their enhanced strength and ability to withstand higher combustion pressures. They are lighter and more durable, contributing to improved engine efficiency and performance.
- Camshafts: Controlling the opening and closing of engine valves, camshafts require precise shaping and high wear resistance. Forged camshafts offer these qualities, ensuring accurate valve timing and long-lasting performance.
- Valve Train Components: Valves, rocker arms, and other valve train components are often forged for increased strength and resistance to fatigue, ensuring proper engine operation and longevity.
Chassis and Drivetrain Components:
The chassis and drivetrain are responsible for supporting the vehicle and transferring power from the engine to the wheels. Forged components are essential in these systems due to the high stresses and dynamic loads they experience:
- Axles: Supporting the weight of the vehicle and transmitting power to the wheels, axles require exceptional strength and toughness. Forged axles provide the necessary durability for safe and reliable vehicle operation, especially in heavy-duty applications.
- Wheel Hubs: Connecting the wheels to the axle, wheel hubs experience significant stress. Forged wheel hubs offer superior strength and resistance to fatigue, ensuring wheel stability and preventing catastrophic failures.
- Steering Knuckles: These crucial components connect the steering linkage to the wheel, allowing the driver to control the vehicle’s direction. Forged steering knuckles provide the necessary strength and reliability for safe and responsive steering.
- Control Arms: Connecting the wheels to the vehicle’s frame, control arms experience significant stresses and vibrations. Forged control arms offer enhanced strength and durability, improving vehicle handling and ride quality.
- Transmission Components: Gears, shafts, and other transmission components experience high torque and repeated stress cycles. Forged components provide the necessary strength and wear resistance for smooth and reliable power transmission.
- Differential Components: The differential distributes power to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. Forged differential components ensure reliable power distribution and prevent premature failure.
Suspension Components:
The suspension system is responsible for absorbing shocks and vibrations, providing a comfortable ride and maintaining vehicle stability. Forged components contribute significantly to the performance and safety of the suspension system:
- Suspension Arms: Similar to control arms, suspension arms connect the wheels to the vehicle’s frame. Forged suspension arms offer increased strength and durability, improving vehicle handling and ride comfort.
- Ball Joints: Connecting various suspension components, ball joints allow for movement and flexibility. Forged ball joints provide the necessary strength and wear resistance for reliable suspension operation.
- Tie Rods: Connecting the steering linkage to the steering knuckles, tie rods are crucial for steering control. Forged tie rods offer enhanced strength and prevent bending or breakage, ensuring safe and responsive steering.
Safety-Critical Components:
Several forged components are essential for vehicle safety, playing a critical role in preventing accidents and protecting occupants:
- Seatbelt Buckles and Components: Forged components are used in seatbelt mechanisms for their strength and reliability in restraining occupants during a crash.
- Airbag Components: Some airbag components rely on forged parts for their ability to withstand the rapid deployment forces.
- Brake System Components: While many brake components are cast, some high-performance or heavy-duty applications may utilize forged parts for increased strength and reliability.
Advantages of Forged Auto Components:
The widespread use of forged components in the automotive industry is due to several key advantages:
- Superior Strength and Durability: Forging refines the grain structure of the metal, resulting in significantly improved strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance compared to other manufacturing processes.
- Enhanced Reliability: The forging process eliminates internal defects, such as porosity and inclusions, resulting in more reliable and consistent parts.
- Improved Safety: The increased strength and reliability of forged components contribute to improved vehicle safety by reducing the risk of component failure.
- Lighter Weight: While offering superior strength, forged components can often be designed to be lighter than comparable parts made from other materials or processes, contributing to improved fuel efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness (Long-Term): While the initial cost of forged components may be higher, their increased durability and reliability can lead to cost savings in the long run due to reduced maintenance and replacement costs.
Conclusion:
Forged auto components are essential for the performance, safety, and reliability of modern vehicles. Their superior strength, durability, and resistance to fatigue make them ideal for a wide range of applications, from engine components and chassis parts to suspension systems and safety-critical components. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, forged components will continue to play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and performance of vehicles on the road. The advancements in forging technology and materials will further enhance the capabilities and applications of forged components in the automotive sector.